Realistic Training in Entrepreneurial Thinking and Action with Hands-On Business Simulation
Definition: What is a corporate simulation game?

A realistic simulation of entrepreneurial activity
- A corporate simulation game sees teams take entrepreneurial responsibility for the successful management of a (simulated) business in a competitive environment.
- Each team uses analysis of the market and competitors as a basis for the development and operational implementation of a business strategy. Their level of success is measured with the aid of key performance indicators (KPIs).
- Corporate simulation games are a highly realistic and efficient means of training management expertise and entrepreneurial thought and action.
- They also foster analytical thinking as well as the ability to resolve conflict and work as a team. Leadership simulation games expand this skill set to include leadership expertise.
Learning by doing
The above-average success of the game-based learning process is the result of the practically oriented, targeted application of knowledge and insights in a highly motivational learning environment.
In addition to experiencing how the various actors and departments within a business interact, participants also learn how to use creative solutions to successfully tackle entrepreneurial challenges in the face of fierce competition – and in turn ensure profitable growth at their simulated business.
In a nutshell
Corporate simulation games are to the development of senior managers and junior executives what flight simulators are to pilot training programmes!
What are the advantages and benefits of corporate simulation games?
What are corporate simulation games used for?
Almost all prestigious companies – including firms listed on the Fortune 500 and German DAX – use corporate simulation games as part of their management development activities. The main reason is their advantages over other teaching and learning formats. The following advantages and benefits have been proven in empirical studies:
Key advantages and benefits
- Increase in powers of analytical thought, including the ability to deal with complexity and uncertainty
- Improvement in teams’ ability to work together and communicate effectively
- Enhanced understanding of the interaction between actors and departments within a business
- Promotion of constructive competition and team spirit (unity)
- Honing of entrepreneurial thought and action (recognizing and exploiting opportunities, taking calculated risks)
- Planning, implementation and review of long and short-term goals and measures
- Enhancement of both rational and intuitive decision-making skills
Putting knowledge into practice
The crucial factor in the success of the learning process is that participants apply their business management acumen in a realistic practical context. This empowers them to internalize new knowledge and insights in a way that other learning methods cannot achieve.
The most important advantage of simulation games is that newly learned knowledge is immediately put into realistic practice. This systematic application of knowledge in a stimulating learning environment is the most efficient way to sustainably internalize expertise. The comparison with the use of a flight simulator for pilot training is therefore very apt.
Areas of application, target groups

Pioneers in the use of corporate simulation games
Corporate simulation games initially established themselves as an element of either general management courses or MBA programmes at prestigious U.S. universities (e.g. Harvard, Stanford, MIT, Yale, UCLA, etc.).
A huge range of methods and versions with varying degrees of difficulty now exists. This has significantly increased the number of potential areas of application and target groups.
Computer-aided and manual simulation games
A large proportion of the games now available take the form of manual simulation games. They offer a number of advantages over computer-aided versions, for example:
- The effort involved in learning how to play the game is considerably lower;
- It is far easier to adapt manual games to company-specific characteristics;
- The way processes are visualized significantly improves the success of the learning process;
- The development of company-specific versions does not require any programming and is therefore far less cost-intensive.
- Specific features and advantages of manual simulation games.
A manual simulation game replicates the simulated company on a game board. This enables participants to literally “grasp” corporate processes. By way of contrast, and to put it in simple terms, computer-aided versions are essentially black boxes that turn one set of abstract numbers into another set of abstract numbers.
In a nutshell
It is considerably quicker and easier to adapt manual simulation games to the needs of the target group, a specific set of KPIs or the company’s market environment. As they are not restricted by the predefined scenarios programmed into computer-aided simulation games, manual games are also characterized by greater flexibility in terms of strategies, tactics and business processes. Another advantage they have over their digital counterparts is that they offer participants more room to manoeuvre when the simulated company experiences unexpected reactions from competitors, customers or the market.
Business Simulation Game for the Industry: "ARTARIS AG"
Concept and Learning Objectives

In the business simulation game ARTARIS AG, the business process of an industrial company is simulated (market analysis – procurement – production – sales – controlling - finance). Four to five teams play, each representing a company in the market.
The team that manages to produce the most profitable products, on the most attractive markets with the best technology against competitors in a dynamic market wins. Key performance indicators from the Balanced Scorecard are used.
The ARTARIS business simulation game is available at various levels of difficulty for different target groups (students, trainees, up to members of executive management).
Procedure:
- In this business simulation game, each team of 4 to 5 participants takes responsibility for the business success of their company.
- Participants take on various roles: Marketing Manager, Production Manager, Purchaser, Controller, Finance Manager, and CEO.
- Roles are rotated during the game so that each participant takes on two to three different responsibilities.
- Each company is in fierce competition with the other teams. What's special about this tactile simulation is that the business processes are replicated on a "game board," making them literally more comprehensible.
- This leads to strong activation with rapid and sustainable understanding (experiencing) of business processes and entrepreneurial decisions.
- Due to this visualization, high competitive pressure, and the need for efficient teamwork, teams usually become highly engaged.
Thus, participants can better comprehend and intensely understand and experience the basic concepts of business administration and the overall context.
Simulation Game Board:
The simulation begins with the acquisition of orders (see figure "Market Research" below). The team must decide which products (A, B, or C) they want to sell in which markets (Central, East, West, South). Once the orders have been won against competitors, the business process starts with the purchase of raw materials, followed by production and storage. Furthermore, there are different technologies available. This requires capital investment decisions. The financial cycle runs in parallel. The effectiveness of planning and its implementation can be seen at the end of the year from the balance sheet, profit and loss statement, and cash flow statement. The team that achieves the best key performance indicators (market share, company value, etc.) over several years wins the game.
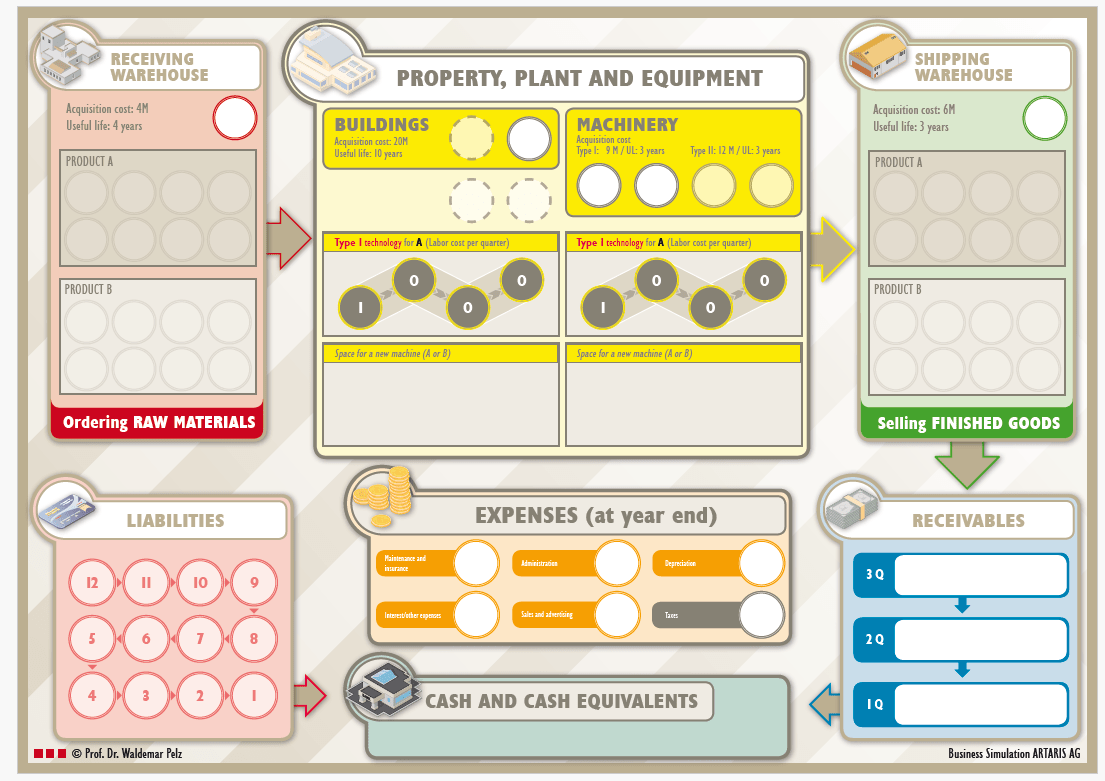
Figure 1: Business Simulation Board of ARTARIS AG
Market Research Data:
One very important decision is which products (A, B, C) should be sold in which markets (Central, East, West, South) based on the following market research data, while being aware that competitors are also seeking attractive markets with highly profitable business opportunities.
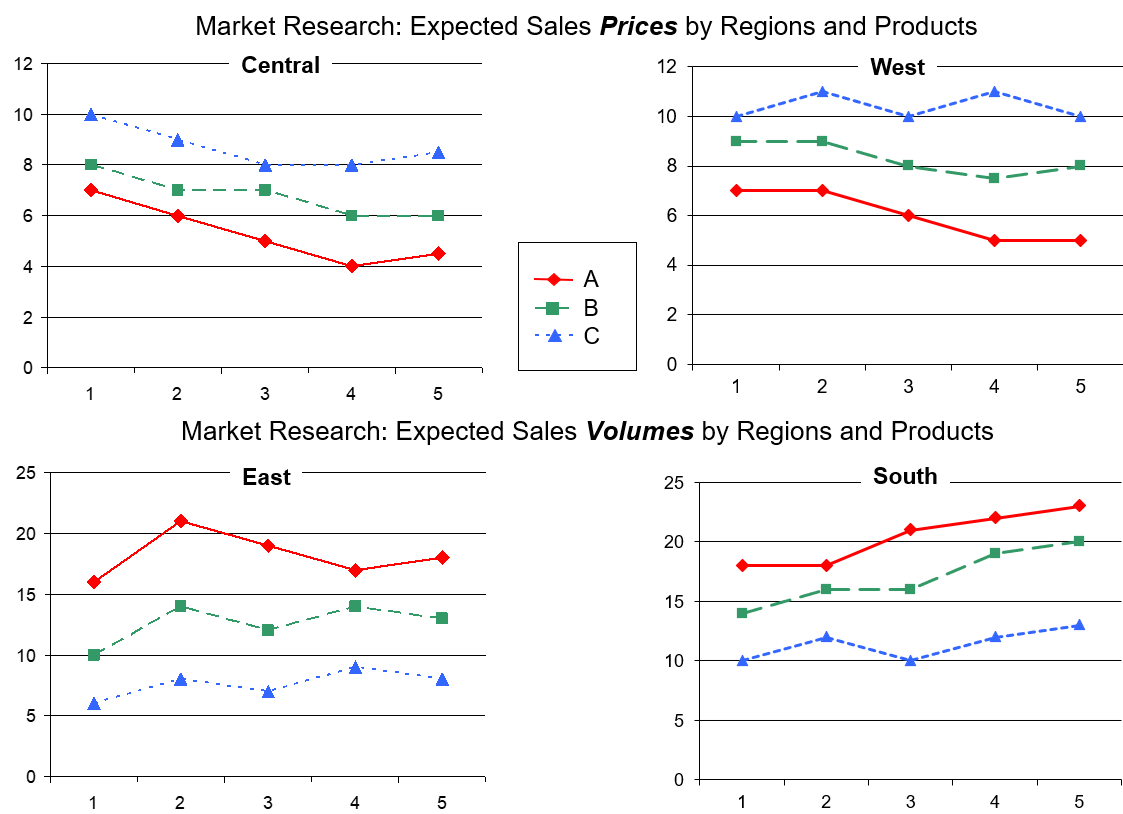
Figure 2: Market Research: Which products (A, B, C) should be sold in which markets (Central, East, West, South)?